Case study: Schools
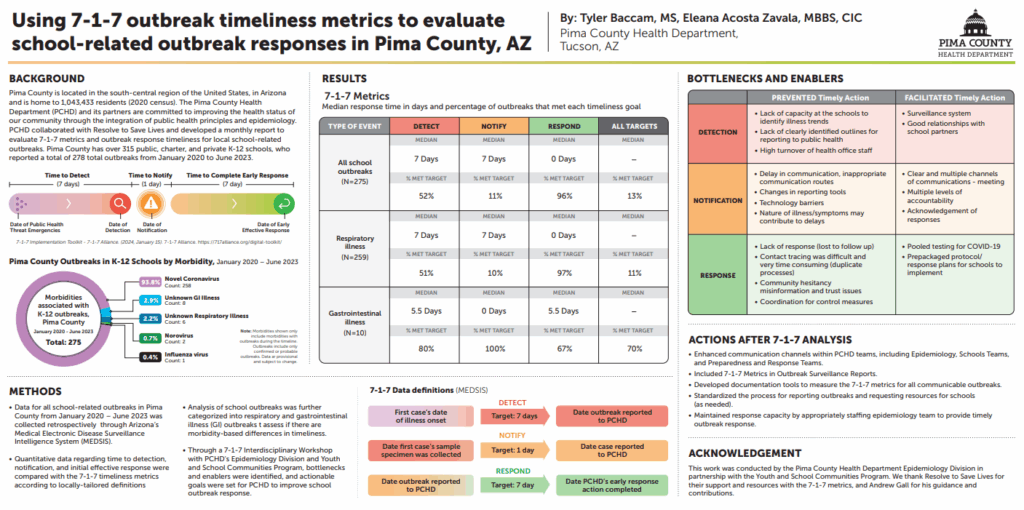
Poster: 7-1-7 outbreak timeliness study—Pima schools demonstrate detection, notification, and response in school-based outbreaks to inform preparedness.
Case study: Varicella
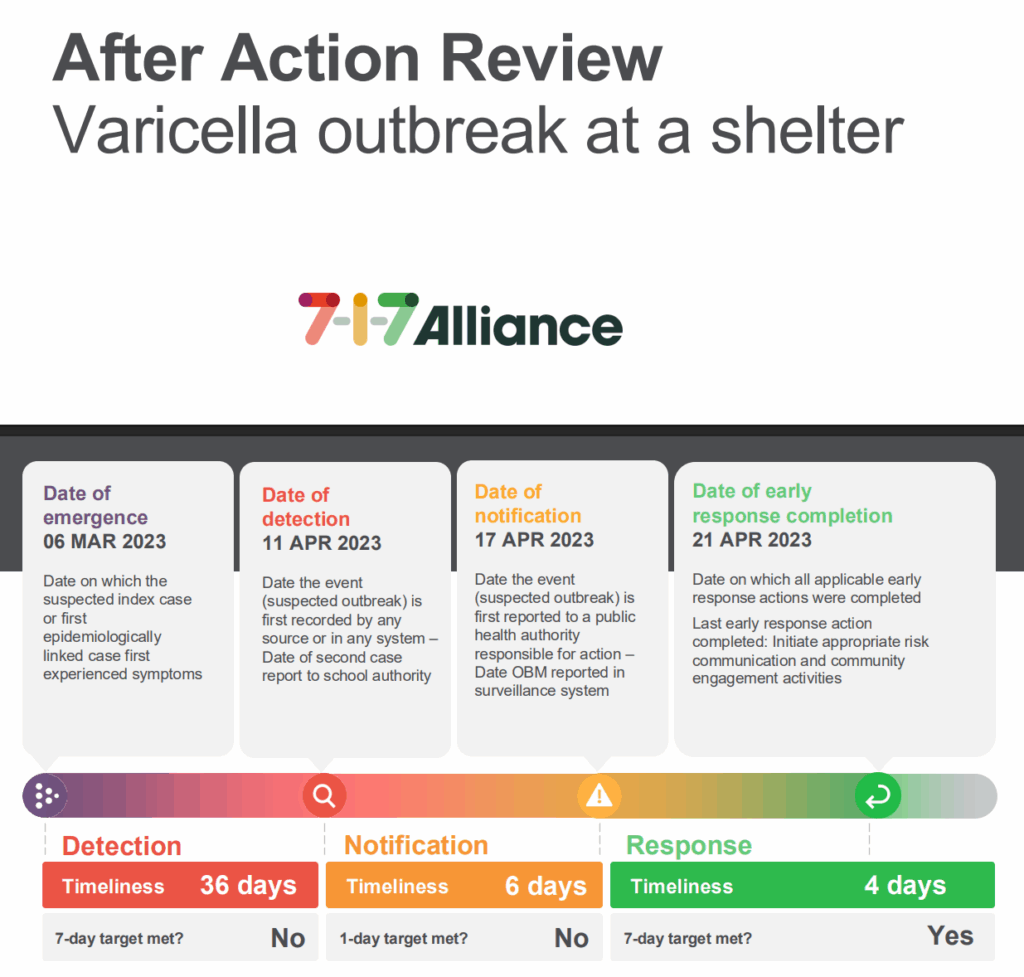
After action review of a 2022 varicella outbreak response in a shelter, noting timely detection and notification, coordination successes, and lessons to strengthen future preparedness.
Case study: Unspecified GI
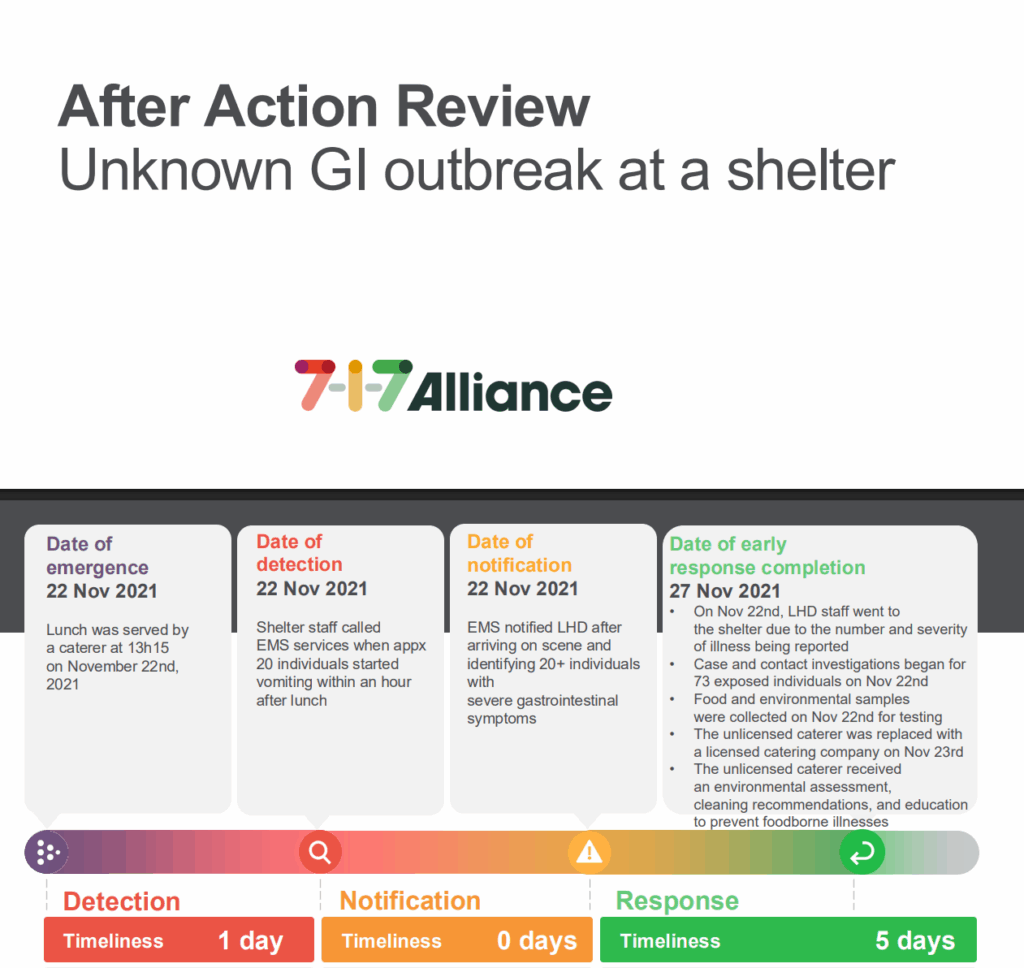
After action review of a 2021 gastrointestinal outbreak response in a shelter, highlighting timely detection, key challenges, and lessons to improve preparedness.
Adopting 7-1-7 in the United States: How the target can strengthen epidemic preparedness

An outline on how 7-1-7 can improve outbreak detection, response, and preparedness in the United States, with lessons from local pilots.
Webinar: 7-1-7 in cities

Webinar held on July 31, 2025 focusing on how 7-1-7 can help strengthen health emergency preparedness and response in urban environments.
Implementing the 7-1-7 target to improve epidemic preparedness and response in Uganda

BMJ Global Health article published on July 13, 2025 co-authored by the 7-1-7 Alliance, country partners and Resolve to Save Lives.
Online course: Using 7-1-7

An interactive deep dive into the use of the 7-1-7 target to take at your own pace.
Epidemics That Didn’t Happen: How South Sudan stopped a cholera outbreak with no reported deaths
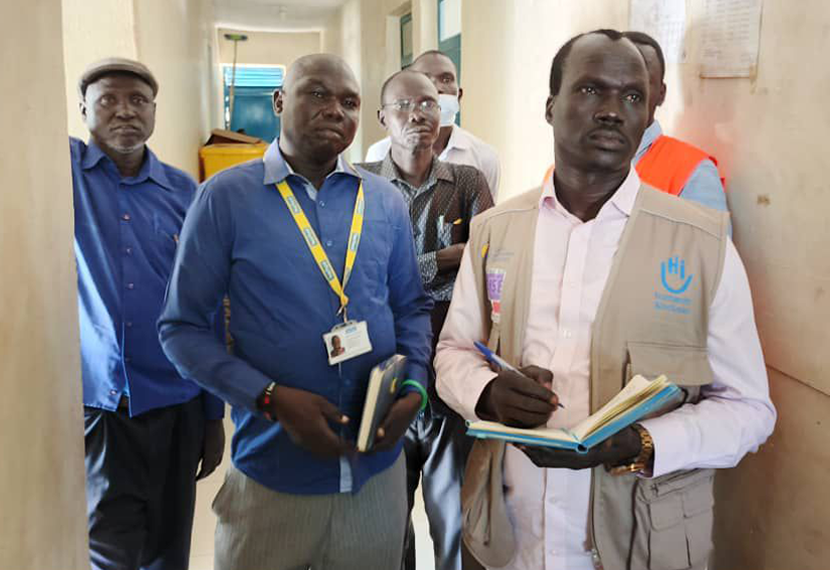

South Sudan brought cholera under control thanks to 7-1-7, a team on high alert and the availability of fast, flexible funds.
Online course: Introduction to 7‑1‑7

An interactive online course to learn about the 7‑1‑7 target at your own pace.
7-1-7 technical training package

All you need to host a four-day 7-1-7 technical workshop.