7-1-7 Digital Toolkit
- English
- Español
- Français
- Português
This toolkit presents stepwise guidance and accompanying tools to support public health authorities at the national or subnational level and partners in adopting and using the 7-1-7 target and the World Health Organization’s Early Action Reviews for continuous performance improvement of outbreak detection, notification and response systems.
Tools, resources and supporting materials are available throughout the toolkit, at the end of each step, and in the resource library. All tools provided are intended to be customized by countries as needed.
Specific country examples are highlighted throughout the toolkit in “7-1-7 in Action” boxes.
The graphic below shows the 7-1-7 lifecycle from adopting the target to using it routinely and advocating using the target. It serves as a visual guide throughout this toolkit. Click through the steps in the graphic to jump to specific toolkit sections.
- Introduction
- Adopt 7-1-7
-
Use 7-1-7
- Step 1 - Collect timeliness data and calculate 7-1-7 performance
- Step 2 - Identify bottlenecks and enablers
- Step 3 - Determine immediate and longer-term actions to strengthen systems
- Step 4 - Routinely consolidate data across outbreaks and monitor progress of actions
- Step 5 - Synthesize and use results for planning and financing
- Advocate with 7-1-7
Introduction
Recent epidemics and pandemics have highlighted limitations in existing measures of health security capacity. They have underscored the importance of evaluating not only the presence, but also the real-time performance of the systems required for early detection, notification, and response.
The 7-1-7 target is based on the idea that every disease outbreak presents an opportunity to learn from real-world experience. The 7-1-7 target uses a simple set of three timeliness metrics to assess and improve detection, notification, and response systems during the early phase of an outbreak:
- ≤ 7 days to detect a suspected disease outbreak;
- ≤ 1 day to notify a public health authority responsible for action;
- ≤ 7 days to complete early response actions.
There are four main uses of the 7-1-7 target:
- Performance improvement: Delays and bottlenecks are easily identified and quantified, and corrective actions are taken to drive system-level improvements.
- Prioritization for action and financing: Data on real-world system performance informs prioritization of available and needed financing (complementing the Joint External Evaluations, the IHR States Parties Self-Assessment Annual Report, and other tools).
- Communications and advocacy: When presented with clear data based on simple metrics, political leaders and donors can easily visualize resource and policy needs—and see how their investments are making an impact.
- Accountability and reporting: Evaluating performance against simple metrics simplifies monitoring and improves transparency in reporting, making it easier to demonstrate the impact of interventions.
Core Principles for the Effective Adoption and Use of the 7-1-7 Target
- 7-1-7 is a continuous performance improvement approach.
- 7-1-7 is intended as a learning opportunity and works best with non-punitive, honest, transparent assessment.
- Each 7-1-7 interval – detection, notification, and early response – is essential.
- The earlier you use 7-1-7, the better.
- 7-1-7 flexibly integrates into existing systems and workflows; planning; and frameworks.
- Engage a broad set of stakeholders because 7-1-7 focuses on addressing a wide range of systemic bottlenecks.
Learn how the 7-1-7 target was established.
Read the landmark Lancet article on 7-1-7 authored by Resolve to Save Lives.
The 7-1-7 target was incorporated to the World Health Organization’s Fourteenth General Programme of Work for 2025-2028 as a joint outcome indicator. 7-1-7 is also the bedrock of WHO’s Early Action Reviews (EARs). EARs use the 7-1-7 target to focus on timeliness and performance improvement of detection, notification, and early response systems in the early phase of an outbreak. 7-1-7 findings from EARs can contribute to discussions during Intra Action and After Action Reviews, and can be used alongside other tools and assessments to help inform and prioritize national/subnational planning.
Adopt 7-1-7
This section outlines the key steps that countries and jurisdictions can take to efficiently adopt the 7-1-7 target.
National vs. subnational adoption
One early consideration is whether to begin adoption at the national or subnational level. This may depend on how centralized/decentralized the country’s governance model is, political will, and other factors. Most countries have first adopted 7-1-7 at the national level, which has helped develop broad support and allowed integration into national-level systems. Some countries, especially federated ones where key public health authority sits at the subnational level, have adopted 7-1-7 in one or more jurisdictions first.
Regardless of the level at which 7-1-7 is first adopted, further scaling 7-1-7 – whether from national to subnational or subnational to national – is important to consider for the next phase of adoption. This is because effective and rapid outbreak detection, notification, and response require engagement and workflows across all levels of government, from local to national. Two key questions to keep in mind when planning 7-1-7 adoption and scale-up are:
- 1) what decision-making powers do the different levels of government have for public health, and
- 2) at what government level are key outbreak, notification, and early response activities conducted/coordinated?
How to approach the adoption steps
Using 7-1-7 for performance improvement is most effective when a broad set of stakeholders is engaged from early on, and when 7-1-7 is incorporated into existing systems. The steps described in this section focus on these key areas of adoption and supporting needs such as leadership, coordination, and training.
The 7-1-7 adoption steps are not strictly sequential. Some steps may be done in parallel, and some may help inform or iterate on a previous step. For example, additional stakeholders missed in the stakeholder mapping or engagement may be discovered through integrating 7-1-7 into workflows. Staff may need to be re-trained based on issues identified from piloting 7-1-7. Or perhaps parts of the stakeholder and existing systems mapping will need to be redrawn after key leadership changes.
The team coordinating 7-1-7 adoption should identify the order in which they will conduct the adoption steps, while remaining flexible and adaptive based on what is learned during the adoption process. Click through the steps on the image below to read more about each step.
Once the key adoption steps have been taken, the 7-1-7 coordination team should develop a 7-1-7 use plan in partnership with stakeholders to help detail, manage, and track the process of using 7-1-7 in the country.
7-1-7 target use plan
1. Developing a 7-1-7 use plan
The 7-1-7 team should prepare a 7-1-7 use plan, under the leadership of the champion and jointly with stakeholders, once the core adoption steps are nearly completed. The 7-1-7 use plan should clearly:
- Identify roles and responsibilities of different teams/stakeholders
- Briefly describe how 7-1-7/Early Action Reviews will be conducted in the country (consider the roles and processes for the key 7-1-7 use steps)
- Define major activities required for 7-1-7 use with appropriate timelines (consider activities around coordination, data collection, performance improvement, national planning, communication and advocacy);
- Propose monitoring and evaluation mechanisms including stakeholder meetings when 7-1-7 performance can be reviewed; and
- Suggest financing mechanisms that may support performance improvement activities.
A draft of the plan should be widely circulated to leadership and relevant stakeholders for their review and feedback. Examples of how the review can be conducted include email, one-on-one stakeholder meetings, existing meetings (e.g., an IHR Technical Working Group), or through a dedicated one-day workshop.
The plan should be finalized after review of stakeholder feedback. The final plan should provide stakeholders with a clear understanding of how the 7-1-7 approach informs performance improvement activities, the processes and timelines for using 7-1-7, and their individual roles and responsibilities.
2. 7-1-7 launch event and communication
After obtaining buy-in of the 7-1-7 use plan from stakeholders, implementing countries/jurisdictions may find it helpful to organize an official launch to announce the adoption of the 7-1-7 target. This can be done in different ways, such as a formal in-person stakeholder convening or a high-level government communication that commits to investment in 7-1-7. Official commitments can provide a basis for increased transparency in future 7-1-7 performance evaluations and help hold stakeholders accountable to each other and to the broader public. They can help galvanize attention, resources and political will to improve the timeliness of outbreak detection, notification and response.
Situate 7-1-7 within the public health system
Finding a place for 7-1-7 within a country or jurisdiction’s health system is largely about the leadership and core team coordinating adoption and use of 7-1-7.
1. Identify a government champion
An early priority in the adoption process is to find a 7-1-7 champion. Champions are government stakeholders who can lead change management, such as individuals with leadership responsibilities for surveillance, response and/or preparedness planning.
Characteristics of a 7-1-7 champion:
- High interest in strengthening health security and the 7-1-7 approach;
- Current or former thought leader in public health;
- Ability to work and collaborate with multiple stakeholders across public health and other sectors;
- Persuasive communicator with strong advocacy and negotiating skills.
Although 7-1-7 adoption should not be burdensome, it may require workflow adjustments, new tools and additional responsibilities for some staff. Experience has shown that 7-1-7 adoption and use are more likely to result in improved epidemic preparedness with the buy-in of at least one government champion who can:
- advocate for 7-1-7;
- provide high-level oversight;
- initiate stakeholder mapping and engagement;
- convene stakeholders to review progress towards goals;
- elevate high-level findings and priorities emerging from routine use of 7-1-7 to leaders.
Once potential champions have been identified and introduced to the 7-1-7 target, it will be important to assess their interest, and if possible, secure a commitment to support adoption and use of the 7-1-7 target.
Government champions have included:
| Uganda | Deputy Director of the National Institute of Public Health, Director of the Public Health Emergency Operations Center |
| Cambodia | Director of the Communicable Disease Department and national spokesperson on outbreak and response at the Ministry of Health |
| South Sudan | Director General of International Health and Coordination at the Ministry of Health |
2. Identify the 7-1-7 coordination team
7-1-7 is most likely to be effective if a single team with a strong technical lead is clearly assigned responsibility to coordinate 7-1-7 adoption and use activities. It is helpful if the champion guides the identification of this 7-1-7 coordination team and has oversight over them.
Ideally, the 7-1-7 team should have responsibility for emergency preparedness and response, and possess both adequate staff and the convening power necessary to bring together a wide set of stakeholders for both 7-1-7 adoption and use activities. For this reason, it is especially helpful for this team to have a strong and well-respected technical leader.
During the adoption phase, this team will coordinate the key activities described in this section of the toolkit and monitor adoption progress. Once 7-1-7 is being used in the country or jurisdiction, they will coordinate the activities described in the Use 7-1-7 section of this toolkit.
Several countries/jurisdictions have found that it has worked well to situate 7-1-7 within Emergency Operations Centers or similar structures where detection, notification, and early response come together and both preparedness and response are prioritized. If 7-1-7 is situated elsewhere in the health system, the 7-1-7 team should proactively involve and build relationships with those in the other areas relevant to 7-1-7. For example, if 7-1-7 is situated on the surveillance side, then extra care may be needed to make sure that response stakeholders are integrated throughout the 7-1-7 lifecycle.
Supporting Tools
- High-Level Introduction to 7-1-7 (PPT)
- Advocacy Brief: Continuous Improvement with 7-1-7 (PDF)
- Advocacy Brief: Advocacy as Easy as 7-1-7 (PDF)
- Advocacy Brief: 7-1-7 for Accountability, Monitoring and Evaluation (PDF)
Map stakeholders and existing systems
1. Mapping of stakeholders
1.1 7-1-7 functions
Early and ongoing support from a broad set of stakeholders is essential for 7-1-7 to be effective. Key 7-1-7 functions that need stakeholder support include overall coordination, capture of data, performance improvement, national planning, and communication and advocacy (see table). Which stakeholders are important for which functions depends on how roles and responsibilities are allocated within the country or jurisdiction. Some stakeholders may be relevant for only one of these functions, while others may be important for several.
| 7-1-7 function | DESCRIPTION |
| Coordination |
|
| Capture of data |
|
| Performance improvement |
|
| National planning |
|
| Communication and advocacy |
|
1.2 Examples of relevant stakeholders
Creating a broad set of stakeholders for 7-1-7 means engaging with different sectors, levels of government (national and subnational), government departments and non-governmental partners. Specific stakeholders relevant to the above 7-1-7 functions will vary by country/jurisdiction, but should broadly include:
- Surveillance and response stakeholders across all key outbreak response pillars from the human health, animal and environmental sectors;
- Preparedness, planning or monitoring and evaluation teams that facilitate International Health Regulations (IHR) assessments and planning;
- Government stakeholders responsible for multi-sectoral coordination, policymakers, and parliamentarians;
- Financing stakeholders, including representatives from ministries of finance (for domestic financing), multilateral development banks and bilateral partners;
- Research and academic stakeholders such as universities and research institutes;
- Other relevant stakeholders, including advocacy groups, civil society and community representatives.
The above stakeholders may play different roles in supporting 7-1-7 functions as described in the table above.
1.3 Stakeholder mapping
Countries/jurisdictions should conduct a stakeholder mapping analysis to identify and document stakeholders needed for 7-1-7. In most cases, stakeholders will not be individuals but rather the relevant team, office, department, etc. This analysis should include which 7-1-7 functions (coordination, capture of data, performance improvement, national planning, and communication/advocacy) the stakeholder has influence over as well as whether the stakeholder is interested in 7-1-7. A country/jurisdiction can use its own tool for this mapping if preferred, or the available 7-1-7 Stakeholder Mapping Tool.
The 7-1-7 coordination team can then use this stakeholder mapping as the foundation for their stakeholder engagement plans.
It is helpful to regularly update this stakeholder mapping, even once the adoption phase is completed, as stakeholders and/or their roles/responsibilities relevant to 7-1-7 may change over time.
2. Mapping of existing systems
Integrating 7-1-7 into a country/jurisdiction’s existing workflows is crucial for efficiency, effectiveness, and sustainability of 7-1-7. The first step is for the 7-1-7 coordination team to map out existing systems, including platforms, tools, meetings, and used for:
- Detecting outbreaks
- Notifying stakeholders when an outbreak is detected
- Collecting information on early response actions
- Convening detection, notification, response stakeholders
- National planning, financing, advocacy
Based on country experience, potential sources of 7-1-7 data on detection, notification, and early response may include initial risk assessments; epidemiologic analyses; outbreak situation reports; rapid response team (RRT) reports; Emergency Operation Center (EOC) meeting notes; event management systems; and Intra-Action Review (IAR) and After Action Review (AAR) reports.
Examples of existing meetings with relevant stakeholders may include response pillar meetings during outbreaks, regular EOC meetings, One Health meetings, annual planning/finance meetings, and other health security meetings.
It is helpful to be as complete as possible in this mapping exercise, and to include all relevant systems (e.g. both paper-based and electronic tools if both are used). A country/jurisdiction can use its own tool or the Existing Systems Mapping tool. The 7-1-7 team can then use this landscape mapping as the foundation for their workflow integration plans.
7-1-7 IN ACTION
Multi-sectoral collaboration during a One Health outbreak in Ethiopia
As one of the 7-1-7 pilot countries, Ethiopia retrospectively applied 7-1-7 to a One Health outbreak they had recently encountered. A case of Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT), transmitted through tsetse flies, was detected in the country in March 2022. Prior to this, HAT had not been reported in the country for 31 years. Staff from the Ethiopia Public Health Institute and the regional level were deployed to support the outbreak investigation and response. The multi-sector One Health response for this outbreak, coordinated by the National One Health Steering Committee, involved a diverse set of stakeholders across multiple levels of government, including for example, public health agencies at the zonal, district, national, and international level (see table).
| Multisectoral | Multi-level | Key Individual roles |
|
|
|
| Multisectoral | Multi-level |
|
|
| Key Individual roles |
|
Core Tools
- Stakeholder Mapping Tool (Excel)
- Existing Systems Mapping Tool (Word)
Engage stakeholders
Early and consistent engagement of a broad set of stakeholders is one of the most important parts of 7-1-7 adoption and can substantially impact the effectiveness of 7-1-7. Stakeholders should be intentionally engaged based on the stakeholder mapping analysis. The more thorough the stakeholder mapping is, the more efficiently and effectively stakeholder engagement can be planned. In particular, those with influence over at least one 7-1-7 function (see previous section on stakeholder mapping) and high interest in 7-1-7 may be able to help galvanize further support amongst stakeholders. Those with influence over 7-1-7 functions but lack of interest in 7-1-7 will require additional targeted engagement.
Stakeholder engagement can be done in various ways:
- One-on-one meetings can be used to introduce the target, tailor messaging to the stakeholder’s interests, and address any questions or concerns about 7-1-7. These meetings can then also lay the groundwork for subsequent stakeholder convenings and adoption activities.
- Small technical meetings can be used to get into the details of adopting and using 7-1-7, especially with the stakeholders that will play important roles in regular use.
- Larger stakeholder convenings can be used to bring together a diverse range of stakeholders, from different government departments to non-governmental partners. This can be a powerful way to get different entities to have a shared understanding of what 7-1-7 is, how it can be rolled out and used in their country/jurisdiction, and what the roles and responsibilities are across the stakeholders.
When engaging stakeholders, it can be helpful to use targeted examples to explain why 7-1-7 is relevant for their work. For instance, examples of how 7-1-7 can be used to improve performance for nosocomial outbreaks may be helpful when speaking with a stakeholder from hospital administration, while highlighting how 7-1-7 can help build evidence for longer-term investments in lab capacity to prevent delays may be useful when speaking with lab stakeholders.
It is helpful to plan how and how often the stakeholder will be engaged based on their role in 7-1-7. Even the more distant stakeholders should be kept regularly updated on 7-1-7 findings so that they can quickly come on board when they are needed.
7-1-7 IN ACTION
Stakeholder engagement and coordination structure in Uganda
Uganda initiated implementation of the 7-1-7 target by first identifying a champion from the Ministry of Health through one-on-one engagements in different departments. The national public health emergency operations center (PHEOC) manager, a senior-level official well-positioned to influence preparedness and response activities, then championed introduction of the target across ministries. Based on the recommendations of the champion, stakeholders working in the areas of coordination, data collection, performance improvement, national planning, and communications and advocacy were approached individually to gauge their interest. This paved the way for subsequent more formal stakeholder engagement and joint implementation planning.
The coordination of 7-1-7 use is now led by the PHEOC, which is responsible for national responses to higher-risk or geographically dispersed events. 7-1-7 use has subsequently been expanded to regional PHEOCs that coordinate responses to smaller and lower-risk events not requiring national support.
Supporting Tools
- High-Level Introduction to 7-1-7 (PPT)
- Advocacy Brief: Continuous Improvement with 7-1-7 (PDF)
- Advocacy Brief: Advocacy as Easy as 7-1-7 (PDF)
- Advocacy Brief: 7-1-7 for Accountability, Monitoring and Evaluation (PDF)
Integrate into workflows
To most efficiently, effectively, and sustainably use the 7-1-7 target for performance improvement, 7-1-7 needs to be integrated into routine systems and workflows within a country or jurisdiction.
A few key areas that should be considered when integrating 7-1-7 into workflows include:
- Data collection
- Data verification and consolidation
- Stakeholder meetings
- Progress tracking
- Synthesis of findings
- Informing other assessments and tools
- National planning, funding and advocacy
Tip: Use your completed mapping of existing systems as a guide when determining exactly how and where to integrate 7-1-7.
When integrating 7-1-7 into each of the workflow integration areas, countries/jurisdictions should consider a few key process questions:
- What needs to be done?
- Who is the responsible officer for it?
- What support do they need to accomplish this?
For example, for data collection, it is crucial to think through how the various data for 7-1-7 are collected and brought together. Who is coordinating this work, and what support, resources, and tools do they need to accomplish this work? For data verification and consolidation, who will be taking the information across outbreaks and putting it into one place? What process will be used for data verification? Will they use the data consolidation spreadsheet tool or something else already in place? For stakeholder meetings, who will be tasked with getting Early Action Reviews and 7-1-7 onto the agenda of relevant meetings? Will they need the backing of the champion or other high-level stakeholders? And so on.
Then across the workflow integration areas, it is useful to think through:
- How and where do the processes overlap?
- What handoff is needed between steps?
Asking and answering the questions above within and across the different workflow integration areas can help the 7-1-7 coordination team avoid gaps in their 7-1-7 workflow plans.
In the following sections, we have included tips that countries have found useful for the key workflow integration areas.
7-1-7 IN ACTION
Data flow in Uganda
In Uganda, the Rapid Response teams, which are supported by the national Public Health Emergency Operations Center (PHEOC), collect information about outbreaks from the district level. Once they get information for an outbreak event, they send it to the regional PHEOC, which supports the districts directly. Once the regional PHEOC has worked with the district and reviewed the data at the regional level, the data gets forwarded to the national PHEOC. The 7-1-7 coordination team at the national PHEOC puts the information into the event consolidation database. This team then does further data verification checks. In this example, there are several areas where a handoff is needed, and several areas of overlap between different workflows.
1. Data collection
Integrating 7-1-7 data collection into existing outbreak data collection first involves determining which system(s) are most appropriate for 7-1-7 data, who is best placed to collect the data, whether definitions of existing variables are aligned with 7-1-7 definitions, and which variables may need to be added for a complete 7-1-7 analysis.
The 7-1-7 Assessment Tool (Word / PDF) includes the key data needed for a 7-1-7 analysis. The fields from this tool can be incorporated into existing templates for risk assessments, rapid response team reports, or event management systems. If no suitable data collection form already exists, the 7-1-7 Assessment Tool can be used as is. Note that this 7-1-7 data tool includes the timeliness metrics and narratives, as well as fields for identified bottlenecks/enablers across the three 7-1-7 intervals and proposed corrective actions to address the bottlenecks.
It is most effective for 7-1-7 data – from timeliness metrics to bottlenecks/enablers and proposed corrective actions – to be collected and recorded during an outbreak by those best positioned to do so, namely public health professionals directly involved in the initial investigation and response. Several countries have found rapid response teams to be very useful for real-time 7-1-7 data collection as those teams are often on the ground investigating the outbreak and coordinating at least parts of the response. Some have integrated 7-1-7 variables into their existing rapid response team templates.
Of the core 7-1-7 data, countries have found that the emergence, detection, and notification milestone dates are often already being collected in their existing systems, though definitions should be compared and aligned. The milestone dates for the early response actions, the milestone date narrative fields, and the text fields for bottlenecks, enablers, and proposed actions are less commonly already included and thus typically need to be added. These are critical for 7-1-7 to be effective for performance improvement. See the 7-1-7 Assessment Tool (Word / PDF) or the Data Consolidation Spreadsheet for examples of key variables to include for 7-1-7.
7-1-7 IN ACTION
Incorporating 7-1-7 into rapid response team reports in Nigeria
Before starting to use the 7-1-7 target, the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC) had developed a report template for use by rapid response teams when investigating a public health event. After adoption of the target, NCDC amended the report template to include the 7-1-7 timeliness metrics and documentation of bottlenecks. Rapid response teams were mandated to provide 7-1-7 data within two- and seven-days after deployment. This facilitated immediate stakeholder review of 7-1-7 performance and identified bottlenecks, enabling stakeholders to take corrective actions to address them and improve the ongoing outbreak response.
2. Data verification and consolidation
The 7-1-7 coordination team is typically tasked with ensuring data quality and consolidating 7-1-7 data across outbreaks into a common database.
Ideally, data verification processes already used in a country/jurisdiction to ensure quality (e.g. completeness, accuracy, etc.) can be adapted to include verification of 7-1-7 data. In some places, data verification will be done by the 7-1-7 coordination team. In others, verification may be done at a lower level, but the 7-1-7 coordination team may conduct final checks. Since milestone date narratives and bottlenecks/enablers are crucial for 7-1-7 analyses but may be new data fields, monitoring these fields for completeness and quality may be especially important.
A platform to consolidate 7-1-7 data across outbreaks is needed to facilitate performance analysis across events. Ideally, these data should be captured in event or project management systems used to track other activities and collect other surveillance and/or response data. If no system already exists, the 7-1-7 Data Consolidation Spreadsheet is available. This spreadsheet is a Microsoft Excel database containing four different tabs:
- Input timeliness data: this tab allows recording of timeliness metrics, bottlenecks and enablers for each outbreak event reviewed against the 7-1-7 target;
- Assess 7-1-7 results: this tab automatically calculates the three 7-1-7 timeliness metrics for each outbreak event and generates tables and graphs that summarize performance across all events entered in the spreadsheet;
- Track corrective actions: this tab allows countries to record all corrective actions identified as well as the responsible authority and implementation status;
- Bottleneck analysis: this tab can be used to consolidate the identified bottlenecks identified and categorize them, facilitating identification of the most common bottleneck types. This analysis has been found useful in helping countries/jurisdictions prioritize longer-term actions for funding.
It is useful to develop a workflow where outbreak data is added to the data consolidation database soon after the outbreak occurs, which allows for the team to obtain corrected information, if necessary, from ground-level staff while the event is still current or recent.
The information in this database should be updated if any new or updated data becomes available.
3. Presentation of 7-1-7 findings to stakeholders
An essential component of 7-1-7 implementation is deciding on an approach for convening key stakeholders to review performance against the 7-1-7 target and discuss actions for future improvement. The 7-1-7 coordination team should select the best fitting meetings to review 7-1-7 findings based on participants, frequency, and meeting purpose. The most effective way to integrate 7-1-7 is to add it as an agenda item to regular meetings. Different approaches can be used to convene stakeholders, as described below:
| VENUE | SETTING | DESCRIPTION |
| Response meeting / response pillar meetings | Emergency Operations Center, National Task Force or Incident Management System meetings | Rapid review of 7-1-7 performance for an ongoing outbreak event in a meeting dedicated to coordinating the response against that event. Presenting 7-1-7 findings here can help recalibrate the response in real-time – one of the great strengths of Early Action Reviews. |
| Routine review meeting | Existing epidemiology or outbreak review meetings held weekly or monthly | Review of 7-1-7 performance for recent outbreak events are incorporated into routinely held meetings that convene key stakeholders, and progress of actions are tracked across ongoing and recent outbreaks.
|
| Multi-event review meeting | Quarterly or annual meeting organized specifically to review 7-1-7 performance | A half- or full-day meeting dedicated to reviewing 7-1-7 performance for multiple recent outbreak events
|
| Planning / finance meetings | Annual or multi-year meetings about national planning and budgeting (e.g. operational planning meetings; National Action Plans for Health Security meetings) | 7-1-7 findings can be used to help inform priorities in national planning and financing |
In addition, the coordination team should determine how and when 7-1-7 findings can be added to other meetings relevant to health security and planning, such as Intra Action and After Action Review meetings, other health security and/or assessment meetings, and meetings where attendance by a member of the 7-1-7 technical team for awareness and engagement may be useful (e.g. One Health coordination meetings).
During the review meetings, 7-1-7 findings for individual disease outbreak events should be presented to stakeholders, with information shared about the outbreak event, the timeliness metrics, bottlenecks/enablers, and proposed actions. The 7-1-7 Event Review Slide template is available for this, or a designated alternative can be developed.
7-1-7 IN ACTION
Convening stakeholders to review 7-1-7 performance in Nigeria
Nigeria is using the 7-1-7 target through its national public health institute, the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention. To ensure effective 7-1-7 implementation, a monthly National Surveillance and Outbreak Review Meeting was reactivated to track timeliness of outbreak detection, notification and response against the 7-1-7 target and as a venue where stakeholders may discuss actions to improve future systems performance.
4. Progress tracking
To ensure performance improvement is achieved, the progress of immediate- and longer-term actions selected through the 7-1-7 process needs to be monitored, ideally using a tracker. For example, the 7-1-7 Data Consolidation Spreadsheet includes a tab for tracking actions. As described in the previous section, this progress should ideally be regularly reviewed during a designated stakeholder meeting. Thus, the relevant workflows, tools, and meetings should be identified to enable this progress tracking.
5. Synthesis of findings
7-1-7 data across public health events should be routinely synthesized to assess performance against the 7-1-7 target. A brief report summarizing this analysis would ideally be disseminated regularly to stakeholders and policy makers. A 7-1-7 Synthesis Report Template is available for this.
The ideal frequency of Synthesis Report dissemination will vary based on the number of public health events, available human resources, and the periodicity of planning activities and funding opportunities that can support completion of corrective actions. At a minimum, a report should be developed and disseminated shortly before each planning cycle. Planning for how and when this type of synthesis and reporting should be done is an important part of 7-1-7 workflow integration.
6. Inform other assessments / tools
7-1-7 findings and recommendations can be useful alongside other tools and assessments for health security. It is useful to identify which other tools/assessments are used and when, and how 7-1-7 findings may be systematically added to the relevant meetings/discussions for these. For example, 7-1-7 bottlenecks and enablers have been mapped to JEE indicators, and guidance is available for how 7-1-7 findings map onto After Action Review discussions.
7. National planning, funding and advocacy
The 7-1-7 target helps identify bottlenecks and corrective actions that can feed into the development of operational (annual) or strategic (multi-year) planning cycles, including National Action Plans for Health Security (NAPHS). Integrating the 7-1-7 target into the NAPHS process and focusing on areas identified for performance improvement help define a more feasible number of priorities per IHR technical area for financing and implementation.
Integrating 7-1-7 into relevant workflows for national planning includes ensuring that:
- Critical stakeholders are involved in event reviews, so that they understand the 7-1-7 target and rationale for the identification of bottlenecks and corresponding actions;
- Corrective actions are assigned to relevant IHR technical areas since, commonly, technical area priorities are defined before consolidation into national plans;
- The 7-1-7 Synthesis Report is disseminated to stakeholders before national planning meetings
- 7-1-7 findings are included in relevant stakeholder meetings for planning and funding (see section 3 on stakeholder meetings above).
Train staff
Those who will be supporting 7-1-7 functions, whether data collection on the ground or high-level national planning, need to be trained on what the 7-1-7 target is and how to use it. The level of training will depend on their role. For example, most high-level stakeholders will need to be made broadly aware of how to use 7-1-7, while technical staff will require more in-depth training on specific tools and workflows. For this reason, it is important to train technical staff once most of the workflow integration is completed. Some of the technical staff will also need to be trained on how to train others (i.e., training of trainers). This is important so that staff can be trained when there is turnover, but also for when there is expansion into other levels such as to subnational teams.
One recommendation based on country experiences is to consider adding 7-1-7 training to existing training opportunities on related topics. This can help reduce travel and other costs while further linking 7-1-7 to existing activities.
The 7-1-7 Alliance has a variety of training packages for countries/jurisdictions and institutional partners. These include an orientation package, an implementer’s package, and training-of-trainers materials. The packages are built from adaptable modules and are highly interactive, with short presentations, hands-on activities, and discussions.
Learn more about training packages.
7-1-7 IN ACTION
Training in South Sudan
South Sudan adopted the 7-1-7 target in 2023. Their 7-1-7 coordination team is based in the Emergency Operations Center and has deep connections to the country’s rapid response teams and One Health program. In addition to the other key adoption steps, they conducted several training activities during the adoption phase.
“Twinning” with Uganda: In July 2023, Uganda hosted a 4-person South Sudan delegation for three days to show them how Uganda uses the 7-1-7 target. The delegation was comprised of the government champion and key members of the coordination team. The visit included meetings, presentations, discussions, and site visits, including to the National Public Health Emergency Operations Center (PHEOC) where 7-1-7 is situated, a regional PHEOC, and the Uganda Virus Research Centre Lab. Learn more about the peer-to-peer experience.
Trainings of leadership and key technical staff: From November to December 2023, South Sudan held three trainings for different levels of stakeholders.
- First, they held a three-day orientation of high-level leadership from different ministries and key partners during which 7-1-7 was presented alongside key health security and planning topics to put the target within the national context.
- Second, they held a three-day technical leadership orientation to sensitize multisectoral technical leads and Line Ministries One Health focal points to 7-1-7.
- Finally, they held a 7-day implementation training for technical officers involved in outbreak detection and response. This included a field simulation, training the staff on the country’s specific 7-1-7 tools and workflows, and applying 7-1-7 to previous outbreaks.
Less than a month after these trainings were completed, South Sudan successfully performed its first Early Action Review on a yellow fever outbreak.
Pilot use
Applying the 7-1-7 target to a few outbreaks during the adoption phase is helpful for several reasons. It helps test workflow integration and allows for iteration as needed. For example, some countries/jurisdictions have discovered gaps in data collection or information flow after piloting 7-1-7. It also provides excellent hands-on training, especially for the 7-1-7 coordination team that will lead many of the 7-1-7-related activities.
Piloting the 7-1-7 target during adoption also provides an additional approach to introducing stakeholders to its benefits. By presenting findings from the pilot to stakeholders, teams have been able to quickly show the power and potential of 7-1-7 to leadership, which has helped to both galvanize support for further use and build momentum to address initial corrective actions.
7-1-7 can be piloted both in real-time through an Early Action Review or retrospectively. When piloting 7-1-7, the coordination team applies the target to recent or current outbreak events and presents their findings to stakeholders, thereby directly demonstrating how the approach can be used to assess system performance and identify required corrective actions. The outcomes of these stakeholder engagements may then be used by the champion and 7-1-7 team to revise their stakeholder mapping to reflect perceived levels of interest, conduct additional stakeholder engagement, inform consensus building and refine roles and responsibilities.
Several countries/jurisdictions that have adopted 7-1-7 have piloted it on 5-10 recent outbreaks. Some have started with retrospective reviews for the first few and then shifted to real-time use of the target. This has helped them move quickly into real-time application of 7-1-7 for new outbreaks soon after the adoption phase.
More details on using 7-1-7 in real-time through Early Action Reviews or retrospectively can be found here in the Use 7-1-7 section of this toolkit.
7-1-7 IN ACTION
A Retrospective Review in Recife, Brazil
Recife, one of the ten largest municipalities in Brazil, conducted a retrospective review of nine events to introduce the 7-1-7 target to a broad group of stakeholders. The Secretary of Health for Recife championed the event, while the Surveillance Department was chosen to coordinate the review. The Surveillance Department selected public health events from the prior two years and compiled 7-1-7 performance data for them. The Secretary of Health then convened a meeting to present the data to a broad group of laboratory, response, information technology, animal health, and environmental health stakeholders. The group discussed the 7-1-7 performance data and agreed on corrective actions that could improve epidemic preparedness. Reviewing public health event performance against the 7-1-7 target was found to be a valuable exercise and it was agreed that the 7-1-7 target should be used to assess future public health events.
Use 7-1-7
This section describes the five key steps for using the 7-1-7 target to improve performance of outbreak detection, notification, and early response systems. These steps demonstrate how the 7-1-7 target can be used for a single outbreak to how 7-1-7 findings across multiple outbreaks can be used for planning and financing.

The World Health Organization provides guidance and tools to conduct Early Action Reviews using the 7-1-7 target, available for download on its website.
Step 1 - Collect timeliness data and calculate 7-1-7 performance
Ideally, 7-1-7 data are captured in real-time or near real-time for each disease outbreak event as part of Early Action Reviews. This maximizes the benefit of using early 7-1-7 findings to inform the ongoing response. However, the capture of real-time data may not always be possible, and it may be necessary to retrospectively collect data after the event response has concluded.
| REAL-TIME | RETROSPECTIVE |
|
|
Retrospective data collection can provide value, but can also be time intensive; locating historical data can be challenging, especially for all response actions; and bottlenecks and their corrective actions could potentially be outdated. For these reasons, we recommend using the 7-1-7 target retrospectively only for recent outbreaks where relatively complete 7-1-7 information is feasible to obtain.
Learn more about conducting retrospective reviews.
1.1 Collect 7-1-7 data for a disease outbreak event
During the adoption phase, the country or jurisdiction should have selected a 7-1-7 data collection tool by integrating the fields from the 7-1-7 Assessment Tool (Word / PDF) into existing systems or by using this Assessment Tool directly. Ground-level staff designated to use the data collection tool should also have been trained on its use.
This section provides detailed definitions of the milestone dates in the Assessment Tool, as well as instructions and examples of how to complete the Assessment Tool.
One of the earliest steps of using the 7-1-7 target is to determine the milestone dates and explain why those dates were selected. This information should be recorded in the designated 7-1-7 data tool. In the 7-1-7 Assessment Tool, these milestone dates and narrative fields are included in Step 1.
Definitions of the key milestone dates are included here.
Collecting the narratives alongside the milestone dates is essential to drive the performance improvement cycle forward because they are crucial for identifying useful bottlenecks and enablers.
Date of emergence
The date of emergence varies by how the disease type is classified in the country/jurisdiction:
- Endemic diseases: the date when a predetermined increase in case incidence over baseline rates occurred (e.g., IDSR alert thresholds).
- Non-endemic diseases: the date when the index case or first epidemiologically-linked case experienced symptoms.
- Other health threats: the date the threat first met criteria as a reportable event, based on existing reporting standards.
Note that the date of emergence is often unknown when a health event is first detected. Epidemiologic information gathered during the outbreak investigation should be used to determine the date, based on whatever information is available. The date may then change as more is learned and earlier cases are identified.
For examples of date of emergence for different event types, see the 7-1-7 Milestone Dates Reference Guide.
Date of detection
The date of detection is the date the public health event was first recorded by any source or in any system.
This may happen at the community or health facility level, through a lab, through the surveillance system, or elsewhere.
For indicator-based surveillance, the date of detection would be when case or incidence data were recorded (e.g., in a log book, case investigation form, laboratory requisition form). For event-based surveillance (EBS), the date of detection would be when the event information was first recorded (e.g., detected by a media scanning system, recorded by a community health worker, recorded by a hotline operator).
Note that detection for the 7-1-7 target is not based on lab confirmation; rather, lab confirmation is an early response action. The date of detection includes suspicion of the event (e.g. entry in a log book, laboratory requisition form, record by community health worker).
For examples of date of detection for different detection types, see the 7-1-7 Milestone Dates Reference Guide.
Date of notification
The date of notification is the date the event is first reported to a public health authority responsible for action.
Oftentimes, the most immediate public health jurisdiction (city, district) will be the public health authority responsible for action and the first public health authority to be notified. Notification of responsible health authorities could be from a clinical setting to a district surveillance officer. In the case of event-based surveillance or when outbreaks are detected centrally, notification to a responsible authority might be from the central level to the subnational level.
For countries that require notification of reportable events to multiple levels of government that are tasked with different actions, the earliest date that any of these public health authorities were notified would be the date of notification. In some guidance, this step may be referred to as ‘reporting’ to a public health authority or district health team.
This step should not be confused with notification to WHO as defined by the International Health Regulations (2005), which is typically only done after local or national public health authorities have become aware of an event.
For examples of date of notification for different scenarios, see the 7-1-7 Milestone Dates Reference Guide.
Date of early response action completion
The date of early response action completion is the latest date on which any of these seven 7-1-7 early response actions are completed:
- Initiate investigation or deploy investigation/response team;
- Conduct epidemiologic analysis of burden, severity and risk factors, and perform initial risk assessment;
- Obtain laboratory confirmation of the outbreak etiology;
- Initiate appropriate case management and infection prevention and control (IPC) measures in health facilities;
- Initiate appropriate public health countermeasures in affected communities;
- Initiate appropriate risk communication or community engagement activities;
- Establish a coordination mechanism.
As shown in the Assessment Tool, the dates for each of these separate early response actions should be recorded, and the date of early response action completion recorded as the last of these dates.
All seven early response actions may not be applicable for some public health events. For example, an event that is determined to be low risk may not require public health countermeasures or risk communication. For events where some early response actions are not applicable, the latest date among the applicable actions should be used as the date of early response completion. “N/A” should be recorded in the data collection platform for these in order to differentiate them from early response actions with missing data.
For examples of dates for each of these 7-1-7 early response actions, see the 7-1-7 Milestone Dates Reference Guide.
1.2 Calculate the three timeliness metrics and determine if the 7-1-7 target was met
The value of determining the dates of emergence, detection, notification, and early response action completion is to calculate intervals between these key events, referred to as timeliness metrics. Public health officials and other stakeholders can use these timeliness metrics to identify whether the processes for detection, notification, and early response were timely for an outbreak event, and whether the event met the 7-1-7 target.
Calculation of the 7-1-7 timeliness metrics
Time to detect = Date of detection – Date of emergence [Target: 7 days]
Time to notify = Date of notification – Date of detection [Target: 1 day]
Time to complete early response actions = Date of early response action completion – Date of notification [Target: 7 days]
The calculated 7-1-7 metrics should be recorded in the designated 7-1-7 data collection tool. In the 7-1-7 Assessment Tool, these are recorded in Step 3.
7-1-7 IN ACTION
Nipah virus in India
On August 29, 2021, the family of a 12-year-old boy who lived near a farm frequented by Pteropus fruit bats brought him to a local clinic in the Kozhikode district of Kerala State with a headache and low-grade fever. Over the next three days, the boy was transferred to one hospital and then another as his condition rapidly deteriorated; he developed serious symptoms including disorientation and loss of consciousness.
With four previous outbreaks of Nipah virus disease reported in India since its emergence—one of which took place in the very same district—district doctors were prepared. Although the boy was much younger than previous cases of Nipah and fell sick outside the typical season for infection, his tell-tale presentation with encephalitis and the clear reporting protocols for symptoms meant that samples were immediately sent to the National Institute of Virology in Pune for testing on September 3. The sample was confirmed to contain Nipah antibodies the following day. Tragically, the boy succumbed to the virus on September 5.
As soon as Nipah was confirmed on September 4, health authorities were alerted and senior health officials across local, district, state and national bodies convened in the Kozhikode district to plan and implement response measures, releasing a detailed action plan and practice manual for all stakeholders on September 5. The group would meet every day—twice a day, at first—establishing a 24-hour Emergency Operations Center in a local guesthouse where they worked together around the clock.
With the help of a multi-disciplinary team from the Indian Government’s National Centre for Disease Control, rapid and exhaustive epidemiological investigations quickly identified 240 of the index case’s contacts and other potential cases in nearby districts; officials also conducted extensive sampling and testing of the fruit bats near his home—all by September 6. The district had learned from previous outbreaks how important contact tracing and case investigation would be to containment efforts, as well as establishing triage centers and isolation facilities to control transmission, a field laboratory for faster test results, and risk communication activities targeting health literacy and behavior change.
The public was informed about Nipah virus transmission and prevention measures through daily press briefings and a “No Nipah” media campaign, and neighboring states were quickly alerted to the potential threat. After a conservative waiting period of 42 days with no new cases detected (twice the length of the potential incubation period of 21 days), India’s Health Minister announced the end of the outbreak on October 17, 2021.
Date of Emergence August 29: The first known case developed a fever and the family sought care.
Date of Detection September 3: The clinician determined that the patient might have Nipah virus, completed a specimen requisition form, and sent the specimen for testing.
Date of Notification September 4: Public health officials were notified of the case.
Date of Early Response Completion September 6: The investigation had been initiated, risk had been assessed, contacts were placed under quarantine, Nipah virus was confirmed, the public had been informed of the outbreak, and a coordination structure had been established.
Time to detect: September 3 – August 29 = 5 days
Time to notify: September 4 – September 3 = 1 day
Time to complete early response: September 6 – September 4 = 2 days
Step 2 - Identify bottlenecks and enablers
While the 7-1-7 timeliness metrics provide a quantitative measure of the performance of systems for surveillance, notification, and early response, on their own they do not provide information about why systems did or did not perform well. Documenting the bottlenecks and enablers of system performance is critical for identifying best practices and the specific systems or processes that require strengthening.
- Bottlenecks are barriers, challenges, or other obstacles that delay detection, notification, or early response activities.
- Enablers are processes, systems, relationships, or other factors that facilitate prompt detection, notification, or early response activities.
Bottlenecks and enablers may be technical, operational, or political.
Note: while much of the discussion for 7-1-7 is focused on identifying bottlenecks for corrective action, the value of enablers should not be underestimated. Enablers show what is working and why, and can help inform discussions on corrective actions for bottlenecks.
2.1 Performing a good 7-1-7 bottleneck/enabler analysis
A good bottleneck/enabler analysis is not difficult to do, but requires having both the right information and knowing how to get to an actionable root cause. Without a good bottleneck/enabler analysis, it is difficult to identify the right corrective actions and the performance improvement cycle breaks down.
Individuals/teams directly involved in the initial investigation and response of an outbreak should discuss and identify bottlenecks, enablers and their root causes based on a review of the 7-1-7 timeliness data, including the narrative fields. This would ideally be done during a participatory session.
The identified bottlenecks and enablers should:
- Be specific: specific bottlenecks/enablers are needed to identify useful corrective actions. Vague bottlenecks and enablers can be nearly impossible to act on or learn from.
- Be actionable: bottlenecks should be identified for which immediate or longer-term actions can be taken.
- Identify root causes: actions should address actionable root causes of delays rather than superficial fixes.
- Focus on the system-level: 7-1-7 is not about blaming or crediting individuals, but rather what is working or not working at the system-level.
| UNCLEAR BOTTLENECK | BOTTLENECKS meeting the criteria |
| “Lab transportation” | “Lack of dedicated vehicle for lab transport to collect samples from health facilities” |
| “Lack of fuel for the vehicles at the clinic to transport samples from the health facility to the laboratory” |
The ‘5 Whys’ approach
The ‘Five Whys’ approach is a simple method for identifying bottlenecks and enablers that meet the above criteria. “Why” is simply asked up to five times in succession until an actionable root cause is determined.
For example,
- I was late to work today. Why?
- I missed the bus. Why?
- I left the house late. Why?
- My alarm did not go off. Why?
- I forgot to set my phone alarm last night. Why?
- My phone was out of charge
- I forgot to set my phone alarm last night. Why?
- My alarm did not go off. Why?
- I left the house late. Why?
- I missed the bus. Why?
This helps identify the root cause of a bottleneck that is specific and actionable, which can then be used to identify a useful corrective action (e.g. a phone charger needs to be kept plugged in at the bedside). “Why” may not need to be asked five times – stop once the above criteria have been met.
Another example is:
- There a specimen transport delay. Why?
- Lack of cold packs for shipping specimen. Why?
- The cold packs were not restocked. Why?
- No order was placed for resupply. Why?
- There was no monitoring mechanism for this type of supply. Why?
- There are no SOPs to direct this work.
- There was no monitoring mechanism for this type of supply. Why?
- No order was placed for resupply. Why?
- The cold packs were not restocked. Why?
- Lack of cold packs for shipping specimen. Why?
If identified bottlenecks or enablers do not meet the above criteria, more information should be sought out from those knowledgeable about what happened during the outbreak. Alternative methods that can be used to conduct a root cause analysis are the fishbone diagram, interviews and focus groups.
2.2 Recording the bottlenecks and enablers
The identified bottlenecks and enablers should be recorded in the tool designated for 7-1-7 data collection. In the 7-1-7 Assessment Tool (Word / PDF), bottlenecks and enablers are recorded in Step 3.
Step 3 - Determine immediate and longer-term actions to strengthen systems
Determining corrective actions is a crucial next step after 7-1-7 bottlenecks and enablers have been identified. Ideally, the initial investigation and response team would propose actions based on the bottlenecks they identified. However, in most settings, these teams may not have the authority or resources to implement the actions, or the actions may reach beyond their work or even sector. Thus, it is recommended that the proposed actions be presented to a broader group of stakeholders to obtain the necessary buy-in and financial resources. Once the stakeholders finalize the list of corrective actions, implementation of the immediate actions should begin as soon as possible. For outbreaks that are ongoing, these actions should inform the incident action plan.
This section provides details of this process, from how to propose clear corrective actions to finalizing and implementing the actions with stakeholders.
3.1 Propose immediate and longer-term actions
Those who identified the bottlenecks and enablers for an outbreak (e.g. initial investigation and response team) are best positioned to propose corrective actions that can resolve the bottlenecks.
Two categories of actions may be surfaced through 7-1-7 use:
- Immediate actions: can be taken immediately with existing funds, staff, and programs.
- Longer-term actions: require additional resources or staffing and may require involvement from different government levels or external partners. These actions should be considered in future national planning (e.g., included in National Actions Plans for Health Security [NAPHS], budgeting, or funding requests to government or external donors).
Actions proposed should be made as clear, specific and realistic as possible, and should be directly linked to a bottleneck. Even if excellent 7-1-7 data are collected and a great bottleneck analysis is performed, performance improvement will still come to a halt if the proposed actions do not address the actual delays, or are too vague or infeasible.
The proposed corrective actions should be SMART:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Achievable
- Relevant
- Time-bound
| UNCLEAR ACTION | CLEAR ACTION |
| “Train Emergency Operations Center staff” | “Design and deliver a three-day training on emergency management protocols for five Emergency Operations Center staff” |
The proposed immediate and longer-term actions should be recorded in the designated 7-1-7 data collection tool. In the 7-1-7 Assessment Tool (Word / PDF), this is done in Step 4.
3.2 Engage 7-1-7 stakeholders routinely for rapid performance improvement
Routinely engaging a broader group of stakeholders is critical to enable the political buy-in to prioritize and resolve bottlenecks and improve detection, notification, and early response systems. This section describes how 7-1-7 data can be shared with stakeholders to support implementation of corrective actions that lead to performance improvement.
Present 7-1-7 results to stakeholders
Key stakeholder meetings where 7-1-7 findings are shared and reviewed are identified during the adoption phase. During the regular review meetings, 7-1-7 findings for individual disease outbreak events should be presented.
This presentation should contain:
- Brief narrative description of the outbreak event;
- Timeline of key milestones (including the four 7-1-7 timeliness milestones) and calculation of the three timeliness metrics;
- Descriptions of bottlenecks and enablers to detection, notification, and early response;
- Proposed corrective actions to address bottlenecks and improve preparedness for future threats.
We recommend that this presentation take approximately 10-minutes, with the purpose of raising stakeholder awareness of the 7-1-7 performance and bottlenecks/enablers and facilitating a discussion of appropriate immediate and longer-term actions to improve ongoing and future responses.
Often, the head of the 7-1-7 coordination team or another member of the team will lead this presentation. The 7-1-7 Event Review Slide template are used for this presentation.
Supporting Tool
- 7-1-7 Event Review Slide (PPT)
Agree on immediate and longer-term actions
The output from this stakeholder review of 7-1-7 performance is a consensus list of corrective actions. The final list of corrective actions should be written using the SMART criteria (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound) described in the previous section.
Actions agreed to be immediate should be designated to a responsible authority provided with the necessary resources to complete them, and start and end dates should be determined. Longer-term actions should be documented for consideration during future planning activities and designated to a responsible authority for follow-through.
All actions and their associated information (e.g. responsible authority, start/end dates, opportunities for planning/funding) should be recorded in the tracker designated during the adoption phase. If the 7-1-7 Data Consolidation Spreadsheet is used, actions can be recorded in the ‘track actions’ tab.
7-1-7 IN ACTION
Identifying immediate corrective actions in the United States
Review of performance against 7-1-7 for a measles case in the United States identified a response bottleneck: it took multiple days to receive the flight manifest for a person infected with measles. After realizing this delay, the local health department determined that it did not have the correct phone number at the airport for requesting flight manifests. This led to an immediate action – someone was assigned to identify the correct phone number. This phone number was updated, which enabled the local health department to receive a flight manifest within one day for a subsequent mpox case. This resulted in rapid investigation during this next outbreak.
Rapid implementation of a corrective action during a yellow fever outbreak in South Sudan. In this video, Dr. Angelo Goup Thon Kouch, who leads the 7-1-7 coordination team in South Sudan, discusses conducting an Early Action Review of a yellow fever outbreak. He and his team presented their 7-1-7 findings at key stakeholder meetings, which resulted in rapid and successful implementation of their proposed action of obtaining and delivering vaccines to the at-risk population.
Step 4 - Routinely consolidate data across outbreaks and monitor progress of actions
4.1 Consolidate 7-1-7 data across outbreaks in a single database
After each outbreak event, information originally captured on the 7-1-7 data collection tool (i.e. the 7-1-7 Assessment Tool (Word / PDF) or a designated alternative) should be stored in the data consolidation database (i.e. the 7-1-7 Data Consolidation Spreadsheet or a designated alternative). In some cases, the data may already be automatically consolidated in an electronic system. If not, the data will need to be entered by the 7-1-7 coordination team.
The data that should be entered for each disease outbreak into the data consolidation database include:
- Key outbreak details (e.g. event name, location)
- Timeliness information: the milestone dates (including for each of the 7 early response actions), associated narratives, and the calculated timeliness metrics
- Bottlenecks and enablers
- Corrective actions and associated information (e.g. responsible authority, start/end dates)
Countries/jurisdictions should actively update the consolidated database, so that as new outbreaks occur, their 7-1-7 data can be quickly entered and checked in this central database.
Core Tool
- Data Consolidation Spreadsheet (Excel)
4.2 Verify the data
Confirm that all data have been entered: Review the list of outbreak events that occurred during the period of interest and confirm that all event data have been entered in the appropriate database(s).
Clean the data: Review the data entered in the databases and check for any missing fields or incomplete information. Obtain additional or corrected information from those knowledgeable about the outbreak, such as subnational staff, rapid response teams, or others who know this information. The sooner verification is done, the easier it is to get corrected information.
In addition, check the calculated values for each of the three timeliness metrics and confirm that any outliers (e.g., negative numbers, large numbers) are correct. For countries using the 7-1-7 Data Consolidation Spreadsheet, this can be done by reviewing outputs on the “Assess 7-1-7 Results” sheet where the timeliness metrics are automatically calculated, and blanks and negative values highlighted.
4.3 Track and discuss progress of actions across outbreaks
Tracking the progress of corrective actions is crucial for effective performance improvement through 7-1-7, and facilitates accountability.
Tracking action progress involves the 7-1-7 coordination team keeping track of the action, which bottleneck it is meant to address, the responsible authorities, the proposed start and end dates of the action, and the implementation status of the action. This can all be done through the ‘track action’ tab of the 7-1-7 Data Consolidation Spreadsheet. If another tool is designated as the action tracker instead, it is important that these data are kept updated and, ideally, in the same database as the overall 7-1-7 data in the consolidated database (i.e. timeliness data and bottlenecks/enablers).
The implementation status of the actions should be regularly assessed and updated in the action tracker. For example, the ‘track action’ tab in the 7-1-7 Data Consolidation Spreadsheet includes an implementation status field with dropdown options of ‘waiting for start date’, ‘in progress’, ‘stuck’, ‘completed’, and ‘deferred (longer-term action).
Regularly presenting the progress on actions to relevant stakeholders means solutions can be discussed for delayed or stuck actions. Ideally this progress reporting can be done in the same meetings 7-1-7 data from new outbreaks are being discussed. This will increase accountability and help ensure that actions are completed in a timely manner and lead to performance improvement.
Some actions initially selected for immediate implementation may remain incomplete and ultimately need to be considered alongside other longer-term actions in future planning activities.
Step 5 - Synthesize and use results for planning and financing
By evaluating the real-world performance of detection, notification, and early response systems, the 7-1-7 target helps generate information that can be used to inform financing and planning decisions. Routine synthesis of 7-1-7 data can help demonstrate progress and highlight persistent bottlenecks. Routine reports (e.g. quarterly, annually) can also provide evidence of performance improvement to stakeholders and feedback on the value of their investments.
This section outlines how consolidated 7-1-7 data can be synthesized, and how the synthesized results can be used to monitor 7-1-7 performance, inform stakeholders of progress, and support prioritization for national planning and financing.
5.1 Synthesize 7-1-7 data
Once the 7-1-7 target has been used for multiple outbreak events, this information can be used to analyze patterns and trends in 7-1-7 performance and bottlenecks across key variables of interest.
The core analyses to synthesis 7-1-7 findings around timeliness, bottlenecks/enablers, and actions are simple to conduct and are described in this section.
Timeliness metrics
Calculating the proportion of events that meet each component of the 7-1-7 target provides stakeholders with a high-level understanding of systems performance. It can help identify whether systems used for detection, notification, or early response can routinely complete timely and appropriate actions.
Core calculations to synthesize timeliness results are:
- # of outbreaks reviewed
- The proportion of events that meet the detection target
- The proportion of events that meet the notification target
- The proportion of events that meet the early response action completion target
- The proportion of events that met all three components of the 7-1-7 target;
Optionally, the proportion of events where the early response action was completed within 7 days can also be assessed for each of the seven early response actions. This helps provide nuanced information on whether some of the early response actions tend to cause more delays than others.
It is recommended that countries present the proportion of events meeting each component of the 7-1-7 target, rather than presenting medians. Median results may be misinterpreted by stakeholders as success when they in fact indicate that only half the events have met the target and critical system strengthening needs may still exist.
Bottlenecks and enablers
Core analyses to synthesize bottlenecks are:
- the most common/frequent bottlenecks
- the most common/frequent enablers
To facilitate prioritization, countries have found it useful to categorize bottlenecks, the most common categories suggesting the areas most likely in greatest need of actions and investment. A bottleneck classification list of 8 bottleneck themes, each further classified into key bottleneck categories, has been developed to support this process.
The ‘Analyze BNs’ sheet of the Data Consolidation Spreadsheet can be used to list bottlenecks and assign them to these categories. A table is then automatically generated showing the frequency of each category of bottleneck.
Immediate and longer-term actions
Core calculations to synthesize progress on actions are:
- Proportion of immediate actions completed
- Proportion of longer-term actions included in national planning documents (e.g. NAPHS)
- Proportion of longer-term actions completed
7-1-7 IN ACTION
Common bottlenecks used to inform actions in Sierra Leone
In November 2022, Sierra Leone applied 7-1-7 retrospectively to assess 16 events and identified several bottlenecks, such as communications constraints between the community level and central level. These included consistent and ongoing challenges related to the call center (such as lack of funding, hotline down, etc.). As a result, the Ministry of Health has been working with partners to strengthen call centers and their operational protocols for improved disease surveillance (i.e. developing SOPs, job aids, etc.)
7-1-7 IN ACTION
Applying 7-1-7 to multiple H5N1 outbreaks helped Cambodia discover common bottlenecks
Cambodia had its first recorded outbreak of H5N1 in 10 years in early 2023 and had five more outbreak events over the next 12 months. For the first few events, they applied 7-1-7 retrospectively, and used the findings to inform discussions during official After Action Reviews. Then, they shifted to using 7-1-7 in real-time through Early Action Reviews for the later outbreak events.
They discovered common bottlenecks emerging across these outbreaks around community and clinical awareness of H5N1 and multi-sectoral collaboration for these One Health outbreaks. They identified immediate actions that were subsequently addressed and longer-term actions that are being implemented to address these common bottlenecks.
Additional variables for disaggregation
The core analyses described above on timeliness metrics, bottlenecks/enablers, and actions can be further disaggregated by key variables of interest. Caution should be used when deciding to conduct these analyses and in interpreting any results if small sample sizes occur for some disaggregation categories.
Variables of interest may include:
- Outbreak event type (e.g. respiratory, food-borne, viral hemorrhagic, etc). The specific categories should be decided by the 7-1-7 coordination team based on country context, with input from stakeholders as needed.
- Geographic area (e.g. region, province, district)
- Time: countries/jurisdictions that have used the 7-1-7 target over multiple reporting periods can evaluate timeliness metrics and performance over time. This can demonstrate progress (or lack thereof) to stakeholders.
Examples of variables of interest when reviewing bottleneck categories include:
- Level(s) of the health system where they occur (e.g., community, health facility, intermediate, or national level)
- 7-1-7 interval (e.g. detection, notification, early response)
Countries have found disaggregation by bottleneck category in this way can help inform where and how corrective actions are implemented to efficiently address common bottlenecks.
Supporting Tool
5.2 Routinely disseminate synthesized 7-1-7 findings to stakeholders
Synthesized 7-1-7 data across outbreak events should be routinely disseminated to a broad set of stakeholders and policy makers both for awareness and to drive forward performance improvement. Countries have found that a synthesis report is useful for such dissemination.
Objectives of this synthesis report include:
- Providing a high-level summary of the most important learnings from 7-1-7 use. These can be prioritized based on observed frequency of bottlenecks or anticipated system-wide impacts of interventions;
- Informing stakeholders of performance against the 7-1-7 target;
- Reviewing progress in completing immediate actions;
- Consolidating and highlighting longer-term actions to inform planning and financing, including integration into NAPHS or similar plans and alignment with funder priorities.
The 7-1-7 Synthesis Report template is available to use, or a designated alternative can be used. The ideal frequency of Synthesis Report dissemination will vary based on the number of outbreak events, available human resources, and the periodicity of planning activities and funding opportunities that can support completion of corrective actions. At a minimum, a report should be developed and disseminated shortly before each planning cycle.
Core Tool
- Synthesis Report template (Word)
5.3 Use 7-1-7 findings to prioritize activities for planning and financing
The 7-1-7 target helps identify bottlenecks and corrective actions that can feed into the development of operational (annual) or strategic (multi-year) planning cycles, including National Action Plans for Health Security (NAPHS). Integrating the 7-1-7 target into the NAPHS process, and focusing on areas identified for performance improvement, helps define a more feasible number of priorities per IHR technical area for financing and implementation. This approach —such as the State Parties Self-Assessment Annual Reporting (SPAR) and Joint External Evaluation (JEE) tools.
To facilitate the process of using 7-1-7 findings to help prioritize planning and financing activities, 7-1-7 corrective actions should be assigned to relevant IHR technical areas since, commonly, technical area priorities are defined before consolidation into national plans. In determining what to prioritize during an implementation period, 7-1-7 bottlenecks and actions can be incorporated as additional items or included as a result of reprioritization of relevant actions from the previous cycle.
7-1-7 findings can also be used to make the case to donors for funding longer-term actions.
The 7-1-7 Synthesis Report is designed to include information needed by stakeholders to support these steps and should be disseminated to stakeholders before national planning and other relevant meetings.
7-1-7 IN ACTION
Using 7-1-7 data to inform activity prioritization during operational planning in Uganda
The Uganda Ministry of Health and Infectious Diseases Institute used the 7-1-7 target to inform the 2023 NAPHS operational planning. Prior to the NAPHS planning workshop, stakeholders convened to review 7-1-7 results and identify common bottlenecks and corresponding actions.
These were then assigned to IHR technical area leads who referenced the data against recommendations from the most recent State Parties Self-Assessment Annual Reporting (SPAR) and Joint External Evaluation (JEE) to determine priorities for the upcoming cycle of NAPHS implementation.
For example, use of the 7-1-7 target identified a bottleneck in the detection of anthrax and viral hemorrhagic fever due to lack of community awareness. This then led to prioritization of the development and distribution of community education materials in the annual operational plan.
Below is the process flowchart adopted by Uganda.
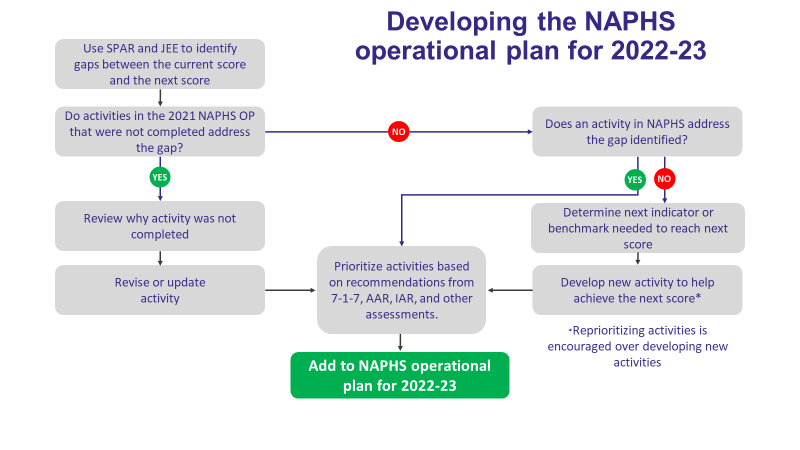
Core Tool
- Synthesis Report template (Word)
Advocate with 7-1-7
The 7-1-7 target is effective at strengthening outbreak detection, notification, and early response systems because it focuses on targeted performance improvement based on findings from real-world outbreaks. But using 7-1-7 results for advocacy has the potential to help create change even beyond this. Results from 7-1-7 can be used to advocate for increased funding and policy changes to strengthen health security more broadly, and for applying the principles of timeliness and performance improvement to other areas of public health and health security. Additionally, 7-1-7 findings can help support accountability.
In this section, we describe how 7-1-7 results can be used more broadly for advocacy, and highlight how key stakeholder groups may use 7-1-7 results to advocate for their goals and promote accountability.
1. Advocating more broadly for funding and policies to strengthen health security
7-1-7 results can help raise awareness of investments or policy changes needed to strengthen health security in a jurisdiction, country, or globally. Regularly applying 7-1-7 to outbreaks not only builds the evidence base for addressing specific or common bottlenecks, but also helps build a case for increased investments in areas related to health security.
7-1-7 IN ACTION
A multi-country retrospective review identifying common bottlenecks
One example of how the 7-1-7 target has been used to raise global awareness of key investments needed for health security strengthening is a retrospective review of events undertaken by five countries (Brazil, Ethiopia, Liberia, Nigeria, and Uganda). The review established that fewer than 25% of outbreaks in these countries achieved the full 7-1-7 target. It then synthesized the most common bottlenecks. The review also identified that delays in detection were primarily at the health facility level, while delays in notification and response were most often at the intermediate/subnational level. The document advocated for increased investment in health facilities and health worker training to improve prompt disease detection and reporting, as well as the strengthening of response mechanisms at the subnational level.
If performance against the 7-1-7 target is not progressing as expected, the data can be used to communicate where additional investments are needed. Using the 7-1-7 target also identifies enablers and those aspects of the system that are working. Demonstrating the success of public health efforts in preventing epidemics and other health threats is a challenge, because the mark of success is when nothing happens. The 7-1-7 target not only makes the successful containment of outbreaks more concrete, but also identifies the specific system factors and investments responsible for success.
7-1-7 IN ACTION
Accelerated responses in Nigeria after a bottleneck analysis
The use of timeliness metrics and the 7-1-7 target can help countries identify catalytic investment needs and communicate their success.
From 2017 to 2019, it took the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC) a median of six days to undertake essential early response action upon detection of an outbreak — and more than one month to respond to one in five (20%) outbreaks. For instance, an outbreak of meningitis in Zamfara (a state in northwestern Nigeria with large agricultural and gold mining industries) went 108 days without a response from NCDC due to a complex interplay of factors.
To remedy this problem, on February 1, 2019, the NCDC established the Revolving Outbreak Investigation Fund (ROIF), which enables the rapid release of funds to investigate, verify and control infectious outbreaks. Since then, the median time to respond to a viral threat has dropped to two days, a 67% improvement over the previous two years. These results have been used by advocates to promote the creation of a rapid response funding line in the federal budget.
Synthesizing timeliness data across outbreaks and countries can also lead to more efficient and impactful interventions that go beyond an individual jurisdiction or country.
Using timeliness metrics to advocate for investments and show returns
Containing yellow fever is a unique challenge. Effective vaccines exist but are in limited supply for a variety of reasons, including their substantial cost. Yellow fever can be difficult to distinguish from other infectious diseases because the virus that causes it is similar to other viruses and can elicit a similar immune response.
Strong diagnostic capacity is required to differentiate yellow fever from other diseases that may require different containment strategies. On the African continent it took an average of 105 days to complete yellow fever testing. Recognizing this challenge, Gavi implemented a program to scale up diagnostic testing capacity in Africa, which quadrupled the number of laboratories able to complete yellow fever testing. To demonstrate the impact of the investment, Gavi highlighted that the average time to complete yellow fever testing had decreased to 39 days by 2020.
In Nigeria, the results were even more dramatic: yellow fever specimens can now be confirmed within 24 hours at the national reference laboratory, accredited by WHO for molecular confirmation in 2021.
“Prior to this investment in diagnostic capacity, it was a huge challenge for countries across Africa to accurately ascertain where yellow fever outbreaks were at risk of breaking out.” – Dr Seth Berkeley, CEO of Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance
2. Promoting the principles of timeliness and performance improvement beyond 7-1-7
While the 7-1-7 target is focused on outbreak detection, notification, and early response systems for infectious disease outbreaks, 7-1-7 findings can help build momentum for others in public health, health security, and beyond to use the underlying principles of timeliness and performance improvement to strengthen systems.
Using timeliness metrics for tuberculosis contact tracing and preventive therapy in India
Inspired by the 7-1-7 target, timeliness metrics were applied for screening and managing household contacts of tuberculosis patients diagnosed by private providers in Chennai, India between November 2022 and March 2023. Their timeliness metrics focused on time for the index case to provide a line-list of potential household contacts after treatment initiation; the time from receiving this line-list to conducting symptom screenings of the contacts; and the time for household contacts to receive treatment or be identified as not needing it. The use of timeliness metrics was deemed “a workable intervention that adds structure to household contact screening and management”.
3. How stakeholders can use 7-1-7 to advocate for their goals and accountability
7-1-7 can be used as an effective tool for communication, advocacy, and accountability
by different stakeholders to advance their goals. Here, we highlight how some key stakeholders may use 7-1-7 for this purpose.
- Government stakeholders:
Government stakeholders have influence over what is included in national budgets and on implementation priorities. The 7-1-7 target allows governments to identify points of failure and bottlenecks across outbreak responses. Because the 7-1-7 target highlights the interplay of various systems, it helps focus accountability rather than just vaguely attributing failed responses. It provides data to help drive decision-making — where to direct attention, training, technical assistance, and funding. Ministries of Health, National Public Health Institutes and local and other officials can reference transparent reporting to advocate for increased investment of domestic resources in systems to improve performance against the 7-1-7 target. They can also use the target to increase and focus support from external donors, while building confidence that funds will be targeted to critical needs and impacts will be measured.
- Civil society and communities:
Civil society and communities have been amongst the most potent forces in advocating for resources and programs to address certain public health issues and in demanding accountability from officials when shortcomings are identified. One of the strongest examples of this is the HIV epidemic. Over the past decades, they have used HIV treatment targets to mobilize action. Civil society and community organizations can have a significant impact in terms of mobilizing funds for outbreak preparedness and response, while tracking how funds are spent and demanding accountability. The 7-1-7 target can further support efforts by advocates to push for increased attention and funding where gaps exist and governments fail to invest adequately in epidemic preparedness.
- Funders and development partners:
Part of the reluctance to fund epidemic preparedness stems from the absence of simple measurements of progress and a lack of prioritized funding needs. As in the case of HIV, synthesized data collected against the 7-1-7 target can help funders and development partners (including foundations, bilateral donors, development banks and technical assistance providers) understand how best to direct resources and structure program funding, while also offering a measure of funding impact. With measurable metrics and an evidence-based list of priority needs — a requirement for bringing major funding on board — the 7-1-7 target helps focus funding contributions on areas of greatest need and builds confidence that funds are well spent.